AI Security Risks
AI is involved in decisions that shape lives, markets, and institutions, highlighting its two-fold value as a powerful asset and a potent source of risk.. AI deployment currently outpaces governance efforts, opening up critical vulnerability avenues, particularly in security risk contexts.
If your AI can be manipulated, stolen, poisoned, or misused, it’s not secure. And if it’s not secure, it’s not ready.
What Do We Mean by AI Security Risks?
AI security risks refer to intentional actions or system weaknesses that can be exploited. These risks don’t show up as technical bugs. They show up as failures in control.
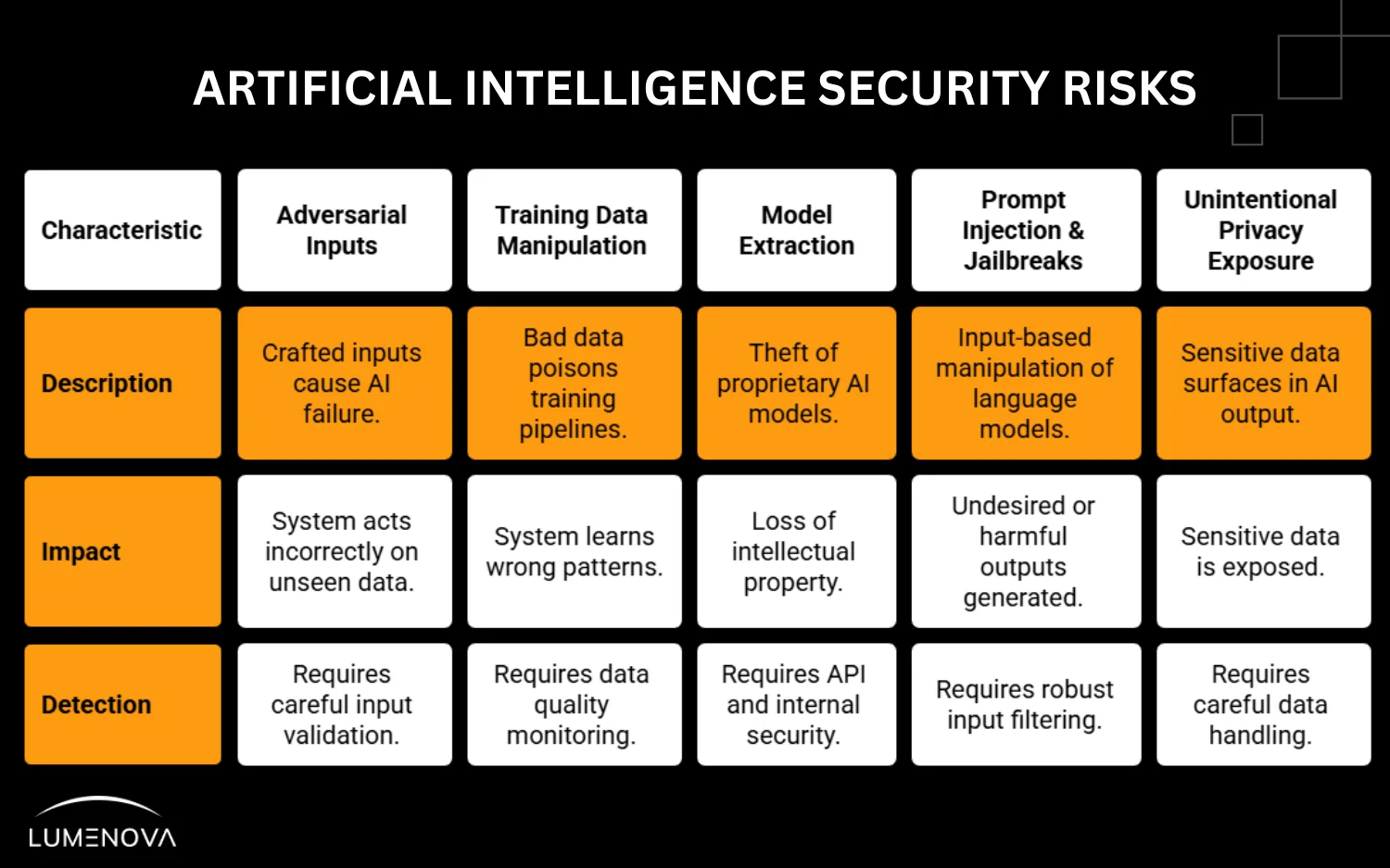
Examples of Current Threats
Adversarial inputs
The crafted input is mis-classified as benign, so the model grants an action (such as releasing sensitive data or approving a fraudulent transaction) that a human reviewer would have blocked.
Training data manipulation
Bad data fed into training pipelines. Once the system learns the wrong patterns, they’re hard to detect and expensive to reverse.
Model extraction
Theft of proprietary models through APIs or internal leaks. Often invisible until the damage is done.
Prompt injection and jailbreaks
Large language models like ChatGPT are vulnerable to input-based manipulation. These exploits are rapidly evolving and difficult to contain.
Unintentional privacy exposure
AI systems trained on sensitive data can surface that data in output. This is a compliance failure, not a bug.
These are all considered AI cybersecurity threats. Some are obvious. Others are subtle and require deeper controls. Few will go away.
Why AI Security Risks Are a Strategic Issue
Security failures in AI systems don’t just break products. They create regulatory exposure, financial loss, and long-term damage to brand and trust.
If an AI system makes a harmful or biased decision, leaks customer data, or breaks under attack, your business isn’t just liable, it’s also unprepared.
This isn’t just a risk for high-profile AI companies. It applies across industries:
- Financial services using AI for credit scoring
- Healthcare systems deploying diagnostic models
- Public sector agencies running language models
- Consumer tech integrating AI assistants at scale
If your organization touches regulated data, real people, or large decisions, you need to manage AI security risks now, not later.
Who Owns AI Security?
Security used to be an IT problem. Now it’s cross-functional. Governance is the only way to scale AI securely.
AI Governance for Security Includes:
- Reviewing training data and inputs before deployment
- Auditing model behavior with internal red teaming
- Building AI monitoring systems for real-time misuse or failure
- Enforcing clear policies around use cases and access
- Maintaining full traceability of data, model versions, and outcomes
Good governance builds resilience. It stops small issues from becoming large-scale or public failures, while aligning AI development with legal, operational, and reputational expectations.
Generative AI and Chatbot Security Risks
Conversational AI comes with additional layers of exposure. Prompt manipulation, identity spoofing, misinformation, and data leakage all increase with generative interfaces.
If your chatbot connects to sensitive systems or shares customer data, then prompt security and response filtering need to be in place from day one. Logging, escalation paths, and human review are not optional.
Responsible AI Isn’t Optional Anymore
AI security is not a checklist. It’s a continual practice. The more powerful your model, the higher the stakes. Responsible AI means embedding security, compliance, and transparency into every stage (from data collection to model deployment).
At Lumenova AI, we build the infrastructure that helps teams monitor, govern, and secure AI systems at scale. Not just to stay compliant, but to stay in control.