AI Guardrails
As Generative AI transforms from a novelty into a core business engine, the need for robust governance has never been more critical. Unchecked models can pose serious threats, ranging from inadvertent data leaks to the generation of harmful content. AI guardrails serve as the essential safety layer in this ecosystem, allowing enterprises to harness the full power of AI while strictly enforcing safety, security, and ethical standards.
What Are AI Guardrails?
AI guardrails are safety mechanisms and control layers designed to monitor, filter, and govern the inputs and outputs of artificial intelligence systems. These safeguards effectively constrain AI models to ensure they operate within ethical, legal, and operational boundaries defined by an organization. By filtering out harmful content, preventing data leakage, and mitigating hallucinations, guardrails serve as a critical defense line for deploying responsible and reliable generative AI.
How Do AI Guardrails Work?
AI guardrails function as an interception layer that sits between the user and the AI model. They evaluate both the user’s prompt (input) and the model’s generated response (output) against a set of predefined rules and logic.
When a user interacts with an AI system, the process typically follows these steps:
- Input Filtering: Before the prompt reaches the Large Language Model (LLM), the guardrail scans it for malicious intent, such as “jailbreak” attempts, prompt injection attacks, or requests for restricted topics. If the input violates a policy, the guardrail blocks it or modifies the request.
- Model Processing: If the input passes the initial checks, the model processes the data and generates a response.
- Output Validation: Before the response is shown to the user, output guardrails analyze the content to ensure it is factually accurate, free from bias or toxicity, and compliant with formatting standards.
- Intervention: If a violation is detected at any stage, the system can refuse to answer, provide a standard fallback message, or regenerate the response to align with safety protocols.
What Type of AI Models Do Guardrails Apply To?
While often associated with the recent boom in Generative AI, guardrails are applicable across the spectrum of artificial intelligence technologies.
- Generative AI (LLMs): This is the most common use case. Guardrails here are critical for preventing hallucinations, toxicity, and copyright infringement in text, image, and code generation models.
- Agentic AI: AI agents capable of taking autonomous actions (like sending emails or executing code) require strict “permission guardrails.” These limit what tools the agent can access and require human-in-the-loop approval for high-stakes actions to prevent cascading errors.
- Traditional Machine Learning (Predictive AI): In standard predictive models (e.g., credit scoring or fraud detection), guardrails typically operate through thresholds on prediction confidence, input schema validation to ensure conformity with expected formats, anomaly detection to identify outliers, and predefined business rules with domain-specific constraints. Additionally, guardrails in this context can include monitoring for data drift, alerting teams when the statistical properties of data diverge from the baseline to signal potential performance degradation or fairness violations.
Why Are AI Guardrails Important?
Implementing robust AI guardrails is essential for organizations looking to move generative AI from experimental phases to production environments. They provide the necessary assurance that an AI agent will not act unpredictably or cause harm.
Key reasons why AI guardrails are critical include:
- Risk Mitigation: They prevent the generation of toxic, hateful, or inappropriate content that could damage brand reputation.
- Data Security: Guardrails detect and block attempts to extract sensitive proprietary information or Personally Identifiable Information (PII) through the AI interface.
- Regulatory Compliance: They help organizations adhere to emerging legal frameworks, such as the EU AI Act, by enforcing strict governance over model behavior and data handling.
- Reliability and Accuracy: By filtering for hallucinations and verifying facts, guardrails ensure the AI provides useful and correct information, which is vital for user trust.
Main Categories of AI Guardrails
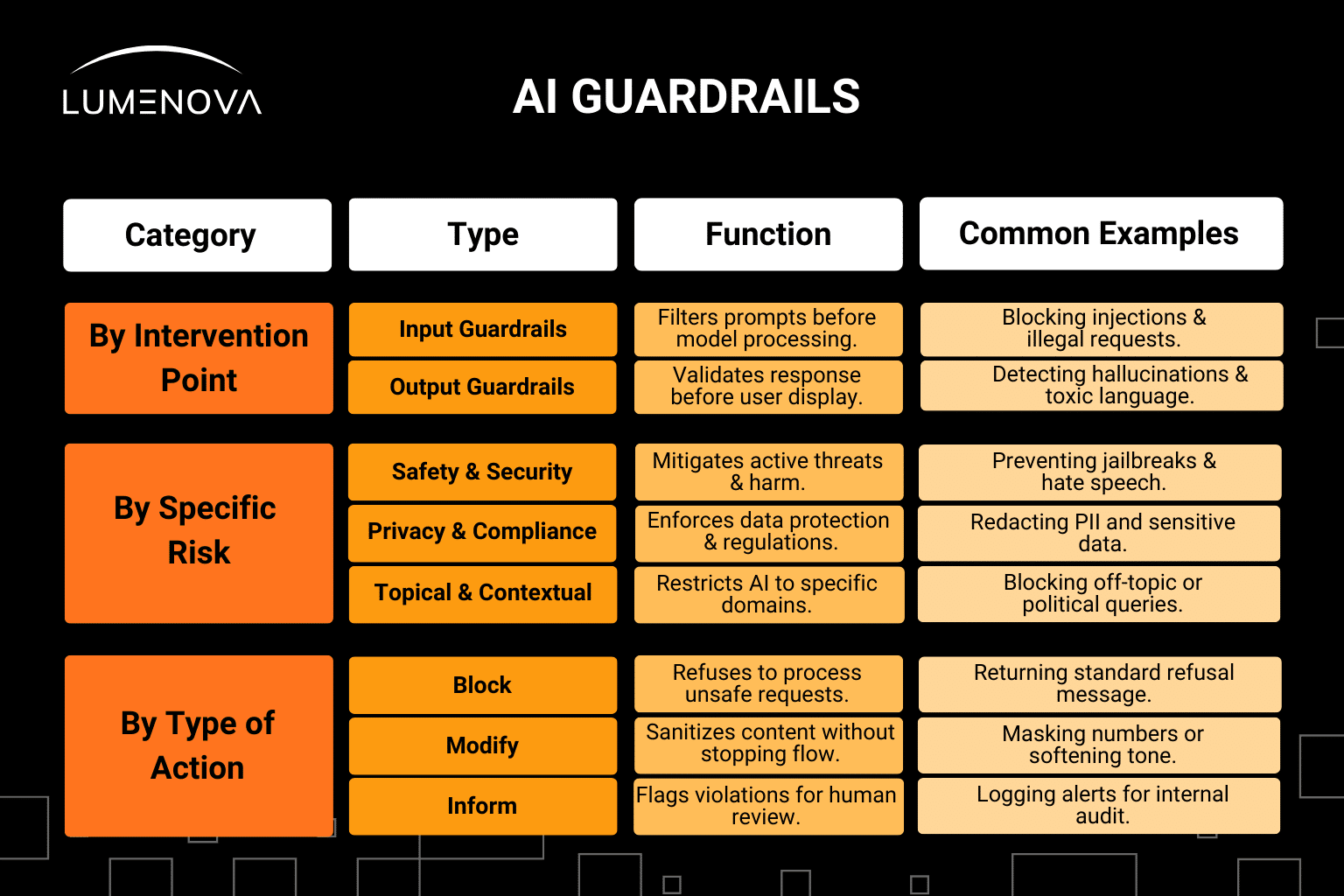
AI guardrails are versatile control layers that can be classified by where they sit in the workflow, what risks they target, and how they respond to violations.
1. By Intervention Point (Lifecycle Stage)
- Input Guardrails: These intercept and analyze the user’s prompt before it ever reaches the model. Their primary goal is to prevent malicious attacks (like prompt injection), filter out restricted topics, and stop sensitive data from entering the system context.
- Output Guardrails: These validate the model’s generated response before it is displayed to the user. They serve as a final quality check to catch hallucinations, block toxic language, and ensure the answer adheres to brand voice and formatting standards.
2. By Specific Risk
- Safety and Security: These guardrails target active threats, such as “jailbreak” attempts, hate speech, or the generation of dangerous code.
- Privacy and Compliance: These focus on data protection, designed to detect and manage Personally Identifiable Information (PII) or prevent the model from violating regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
- Topical and Contextual: These keep the AI “in its lane”. For example, a specialized financial banking bot would be restricted from answering questions about medical diagnoses or political opinions.
3. By Type of Action
- Block: The strictest response, where the system refuses to process the prompt or generate an answer (e.g., returning a message like ”I cannot assist with that request”).
- Modify (Mask/Sanitize): The guardrail alters the content to make it safe without stopping the interaction. Common examples include masking credit card numbers or rewriting a response to soften the tone.
- Inform (Log/Alert): The system allows the interaction to proceed, but flags the potential violation in a log for human review or displays a warning to the user. This is often used during internal testing or for low-risk policy violations.
How Can Enterprises Develop AI Guardrails?
Developing effective guardrails requires a systematic approach that balances safety with system performance.
- Risk Assessment: Organizations must first map out specific risks relevant to their use case. A healthcare chatbot requires different safety thresholds than an internal coding assistant.
- Policy Definition: Clear guidelines must be established regarding what constitutes “safe” and “unsafe” behavior. This includes defining restricted topics, toxicity thresholds, and data privacy rules.
- Technical Implementation: Developers can implement guardrails using programmable frameworks that allow for creating custom validators and rules. To ensure these safeguards are architected for scale and complexity, the Lumenova AI Forward Deploy Team works directly with organizations to custom-build and integrate these protections into production environments.
- Adversarial Testing (Red Teaming): Before deployment, teams should actively try to break the guardrails (“red teaming”) to identify gaps in coverage and refine the rules.
- Continuous Monitoring: Guardrails are not “set and forget.” Enterprises must continuously monitor logs for false positives (blocking safe content) and false negatives (allowing unsafe content) to tune the system over time.
Secure Your GenAI Models with Lumenova AI
Empower your organization to harness the full productivity potential of Generative AI without compromising on security. Lumenova AI’s Generative AI Guardrails provide the essential defense line needed to confidently deploy AI systems, mitigating risks ranging from accidental data leakage to toxic hallucinations. By implementing real-time protections – including sensitive information filters, prompt injection detection, and word filters – Lumenova AI helps you enforce acceptable use policies and build stakeholder trust. Ensure your AI remains ethical, compliant, and strictly aligned with your brand standards using our comprehensive AI governance solutions. Request a demo today.
Frequently Asked Questions
Fine-tuning involves retraining the model’s internal parameters to learn new behaviors, whereas guardrails are external control layers that enforce rules on inputs and outputs without altering the model itself.
Yes, adding validation layers can introduce a slight delay. However, optimized guardrails are designed to execute checks in milliseconds, ensuring the impact on user experience is negligible.
No security measure is foolproof. While guardrails drastically reduce risks like jailbreaks and toxicity, they should be used in combination with red-teaming and continuous monitoring for comprehensive protection.
Yes. Even internal tools carry risks, such as accidental data leakage, the generation of insecure code, or providing employees with hallucinatory information that could lead to poor business decisions.
A jailbreak is a specific type of prompt engineered by a user to trick an AI model into bypassing its safety rules and generating restricted or harmful content.